Overview
The automotive landscape refers to the overall structure of the automotive industry, involving various tiers and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
Tiers: The automotive industry is often divided into tiers, which represent different levels of suppliers. These tiers are based on the complexity and significance of the components or systems they provide to OEMs.

OEMs and Car Manufacturers
OEMs are the companies that design, manufacture, market, and sell automobiles. They are at the top of the automotive industry hierarchy. OEMs are the major car manufacturers at the top of the supply chain pyramid.
They focus on designing vehicles, ordering parts from suppliers, and assembling the final products. The average car contains around 30,000 parts sourced from various suppliers.
Suppliers Ecosystem
– Tier 1 suppliers: These companies play a major role in the automotive supply chain as they directly supply components or systems to OEMs. Tier 1 suppliers often specialize in a specific type of component, such as engines, transmissions, or infotainment systems. Examples of Tier 1 suppliers include Bosch, Continental, and Magna International.
– Tier 2 suppliers: These suppliers provide components or subsystems to Tier 1 suppliers rather than directly to OEMs. They often specialize in niche components and play a critical role in the overall supply chain. Examples of Tier 2 suppliers are Denso, Lear Corporation, and ZF Friedrichshafen AG.
– Tier 3 suppliers: These suppliers provide raw materials or basic parts to Tier 2 suppliers. They are usually smaller and more specialized companies, such as steel and plastic manufacturers. Examples of Tier 3 suppliers include Nippon Steel, BASF, and Dow Chemical Company.
– System Integrators
The role of a system integrator involves understanding the requirements and specifications of a vehicle project and coordinating the design, development, and implementation of various subsystems. They ensure that all the subsystems work together seamlessly to achieve the desired performance, functionality, and safety standards. System integrators collaborate with suppliers, engineers, and other stakeholders to select and integrate the best components and technologies. They also manage the interfaces between different subsystems, conduct testing and validation, and address any issues or challenges that arise during the integration process. It is important to know that some of the Tier-1s take up the systems integrator roles like Bosch, ZF etc. Where as sometimes the Systems Integrators work only on integrating systems from various suppliers, like HLE Klemont, KPIT, Hyundai Mobis, etc. [2], [3]
Autonomous Driving & SDV
Software-defined vehicles have a significant impact on the automotive industry [3], [4]. Software-defined vehicles (SDVs) have greatly contributed to advancements in autonomous vehicles in several ways:
- Integration of Sensors and Algorithms: SDVs play a crucial role in integrating the sensors and algorithms needed for autonomous driving. They provide computing power and software infrastructure to process and analyze data from sensors like cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors. This integration allows for real-time perception and decision-making, enabling autonomous driving capabilities.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: SDVs leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance autonomous driving capabilities. They use AI algorithms to learn from data and make predictions, improving perception, decision-making, and vehicle behavior in complex driving scenarios. By continuously updating and refining these algorithms, SDVs can adapt to changing conditions and improve their autonomous performance over time.
- Over-the-air Updates: SDVs enable over-the-air updates, allowing for remote software upgrades and improvements. This is particularly important for autonomous vehicles, as it enables automakers to enhance autonomous functions, add new features, and address any software-related issues without needing physical interventions. Over-the-air updates enable continuous improvement and keep autonomous vehicles up to date with the latest advancements.
- Connectivity and V2X Communication: SDVs facilitate connectivity and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, which is crucial for autonomous driving. Connected autonomous vehicles can receive real-time information about road conditions, traffic, weather, and other vehicles, enhancing their perception capabilities. SDVs enable this connectivity, ensuring seamless communication with external devices, infrastructure, and other vehicles.
- Data Collection and Analytics: SDVs collect vast amounts of data from sensors and other sources during autonomous driving. This data is valuable for training autonomous algorithms, improving perception, and enhancing the overall performance of autonomous vehicles. SDVs provide the infrastructure to collect, store, and analyze this data, enabling continuous learning and improvement in autonomous driving systems.
- Safety and Redundancy: SDVs contribute to the safety of autonomous vehicles through redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms. They enable multiple sensors and redundant control systems to work together, ensuring safety and reliability in autonomous driving. SDVs also play a role in providing real-time diagnostics and monitoring systems, helping detect faults or malfunctions and ensuring the safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
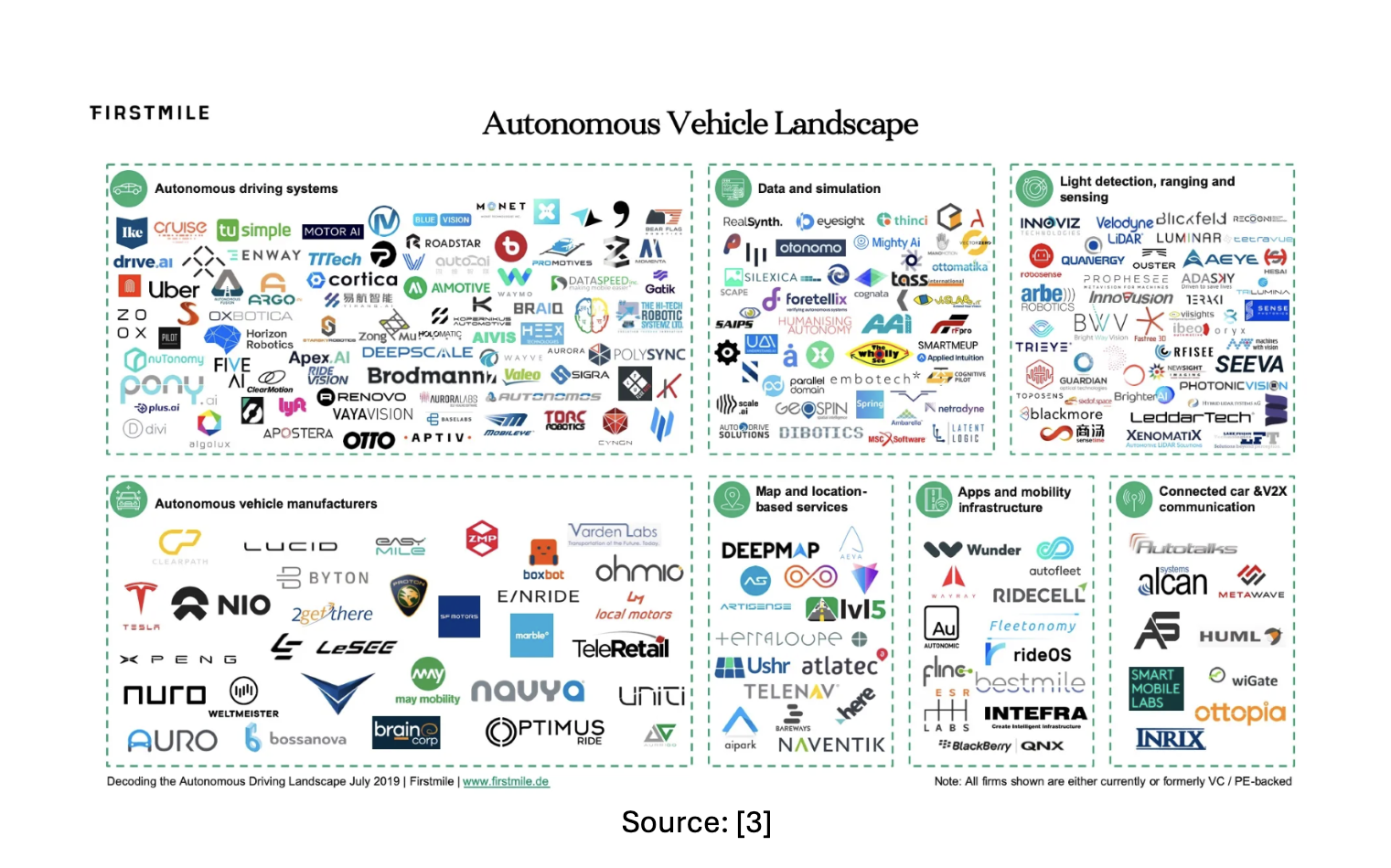
Key Changes
- Vehicle Connectivity: Software-defined vehicles enable seamless connectivity and communication with external devices, infrastructure, and other vehicles. This connectivity allows for advanced features like over-the-air updates, real-time diagnostics, vehicle-to-vehicle communication, and integration with smart city infrastructure. It enhances safety, efficiency, and convenience for drivers and passengers.
- Enhanced User Experience: Software-defined vehicles offer improved user interfaces, intuitive controls, and personalized settings. Advanced infotainment systems, voice assistants, and smartphone integration provide a more enjoyable and convenient driving experience. Such features also enable automakers to offer subscription-based services and applications.
- Autonomous Driving: Software-defined vehicles play a crucial role in enabling autonomous driving capabilities. They integrate complex algorithms, sensors, and artificial intelligence systems to analyze and process vast amounts of data from various sources. This allows for features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, automatic parking, and eventually, fully autonomous driving.
- Data and Analytics: Software-defined vehicles generate massive amounts of data. Automakers can utilize this data to gain insights into customer behavior, vehicle performance, and predictive maintenance needs. This information helps in improving vehicle design, customizing services, and enhancing overall customer experience.
- Cybersecurity: With increased connectivity and reliance on software, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern for software-defined vehicles. Automakers need to prioritize robust security measures to protect against potential cyber threats and ensure the privacy and safety of vehicles and their occupants.
- New Business Models: Software-defined vehicles open up opportunities for new business models, such as mobility services, shared ownership, and subscription-based vehicle features. Automakers can offer flexible ownership options, on-demand services, and access to a wider range of features and functions through software updates and customization. [5], [6]
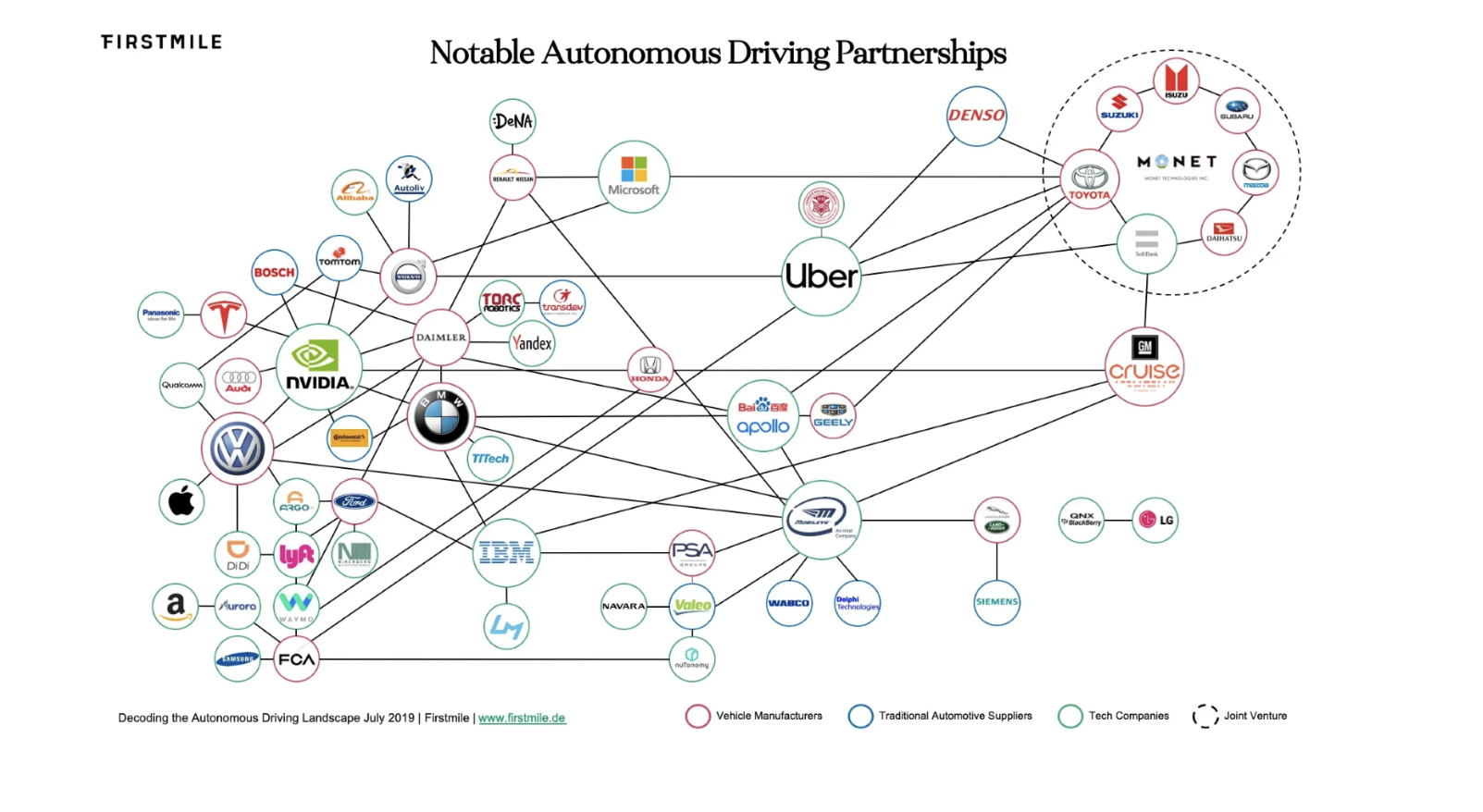
Collaboration and Partnerships
The software-defined vehicle landscape necessitates increased collaboration between automakers, technology companies, and other stakeholders. Partnerships are essential to leverage expertise in software development, connectivity solutions, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Automakers are forming alliances and working with tech giants to accelerate innovation in this area.
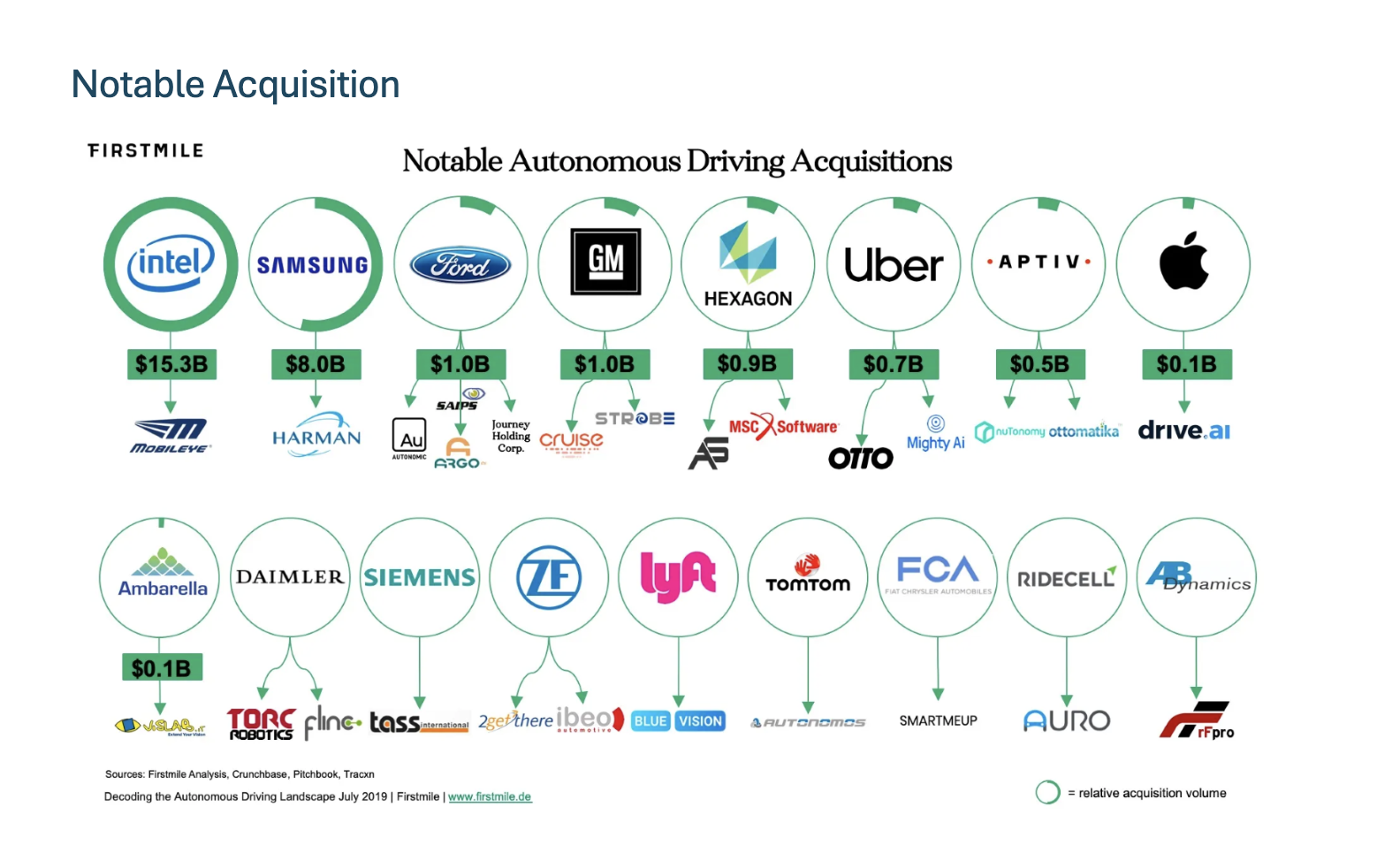
Notable Acquisition
Summary
The automotive industry is undergoing significant changes due to advancements in autonomous vehicles and the rise of software-defined vehicles (SDVs). SDVs integrate sensors, algorithms, machine learning, and connectivity to enable autonomous driving capabilities. They also facilitate over-the-air updates, data collection, and analytics, and enhance the user experience and vehicle connectivity.
Key changes brought about by SDVs include increased vehicle connectivity, improved user experience, the enablement of autonomous driving, data and analytics-driven insights, cybersecurity concerns, and the emergence of new business models such as shared ownership and subscription-based services.
To navigate this changing landscape, collaboration and partnerships between automakers and technology companies are becoming increasingly important. These partnerships allow for the exchange of expertise in software development, connectivity solutions, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Several notable acquisitions have also taken place in this space as companies aim to strengthen their capabilities and accelerate innovation in SDVs.
References
[1] “(20) Shunqiao Sun on X: ‘Building Blocks of Autonomy https://t.co/m2TyUl07Jk’ / X.” Accessed: Jul. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://x.com/ShunqiaoSun/status/740584404444053505
[2] “Shunqiao Sun on X: ‘Building Blocks of Autonomy https://t.co/m2TyUl07Jk’ / X.” Accessed: Jul. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://x.com/ShunqiaoSun/status/740584404444053505
[3] “Decoding the Autonomous Driving Landscape | by Firstmile VC | Medium.” Accessed: Jul. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@firstmilevc/avlandscape-8a21491f1f54
[4] “Future Of Autonomous Vehicles: Self-Driving Cars Explained.” Accessed: Jul. 01, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.forbes.com/sites/technology/article/self-driving-cars/
[5] “What is an Autonomous Car? – How Self-Driving Cars Work | Synopsys.” Accessed: Jul. 01, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.synopsys.com/automotive/what-is-autonomous-car.html
[6] “The Partnerships Shaping The Future Of Autonomous Driving – CB Insights Research.” Accessed: Jul. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.cbinsights.com/research/autonomous-driving-business-relationships/

